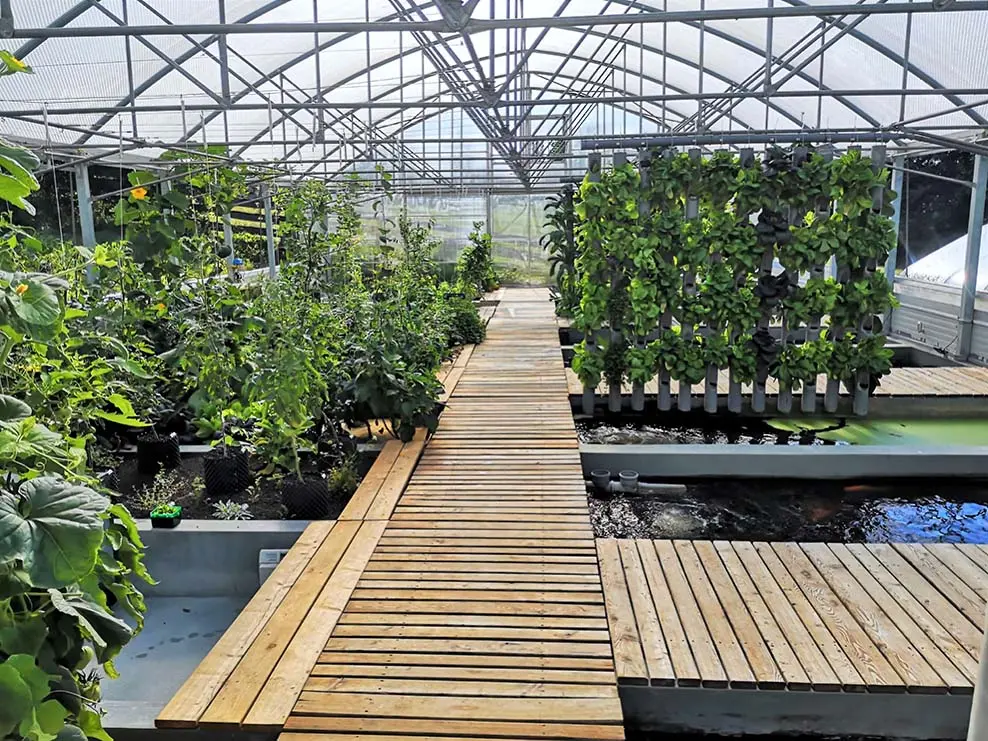
Make your decision
Big decisions in life are best made carefully. We want to help you with this.
We will provide you with the information and input you need to make the right decision for you. Take your time. After all, it's about your future.
We want you to understand what aquaponics actually is and why aquaponics will play an important role in feeding humanity in the future. We will show you why we believe that our aquaponics systems are the ideal solution for farmers in particular, how much you need to invest and how you will be rewarded for doing so. And, of course, we will give you an insight into the operations of existing customers.
And if you still have doubts as to whether the production of fish and vegetables is something for you, whether you are capable of butchering and filleting the fish, and whether the direct marketing of fish and vegetables in your region works, then take a small intermediate step first. Build your first compact but professional aquaponics system and start gaining experience with very little risk.
Success ultimately comes down to three words: Just do it.
What exactly is aquaponics?
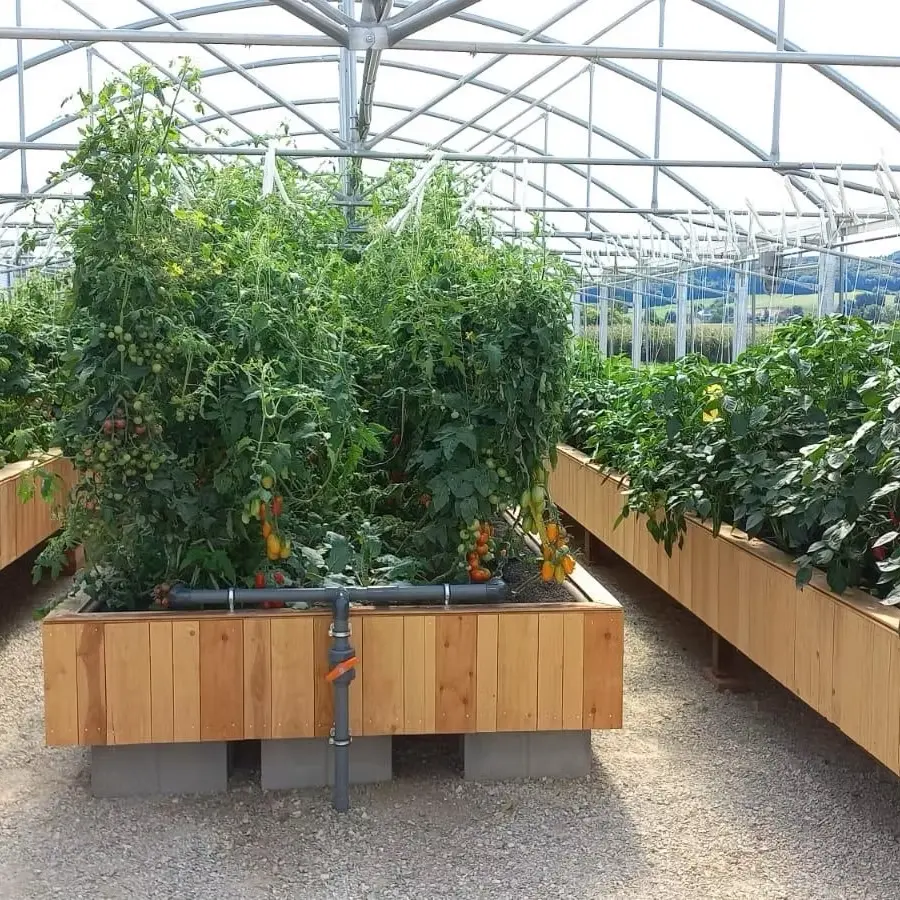

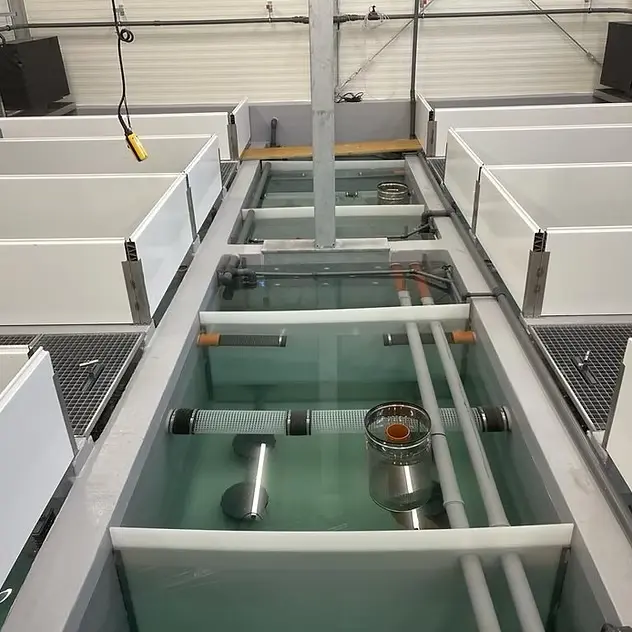
Real working systems

Key factors for success
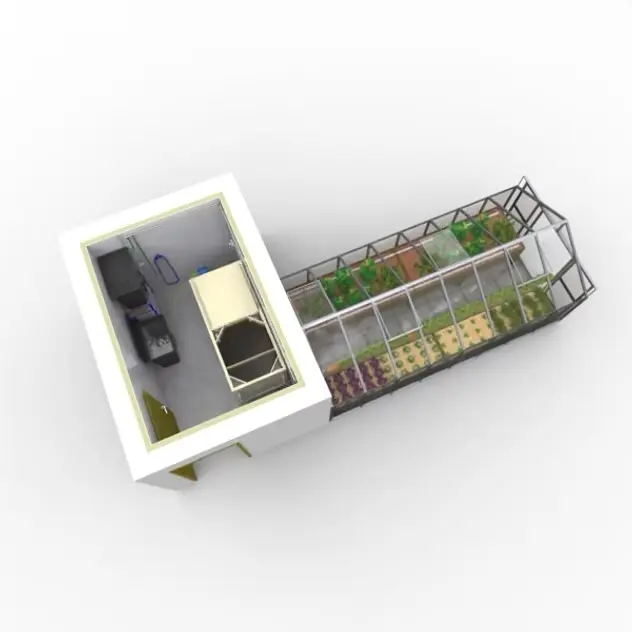

Start with low risk
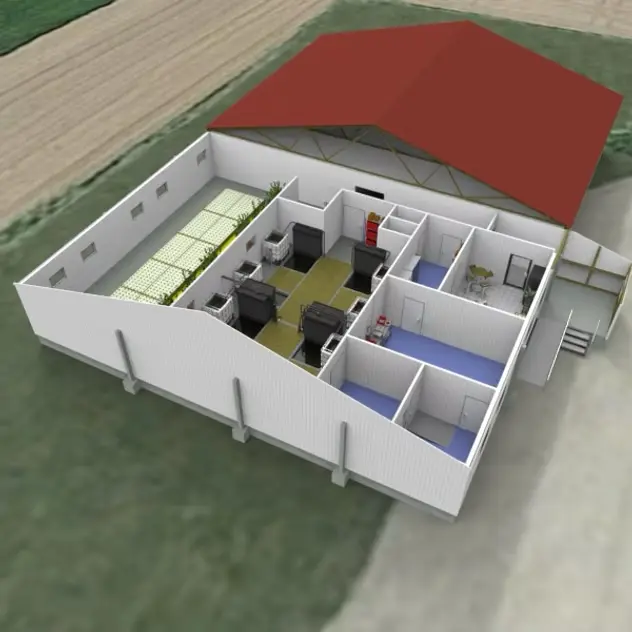

Turning old into new

Do you need advice?
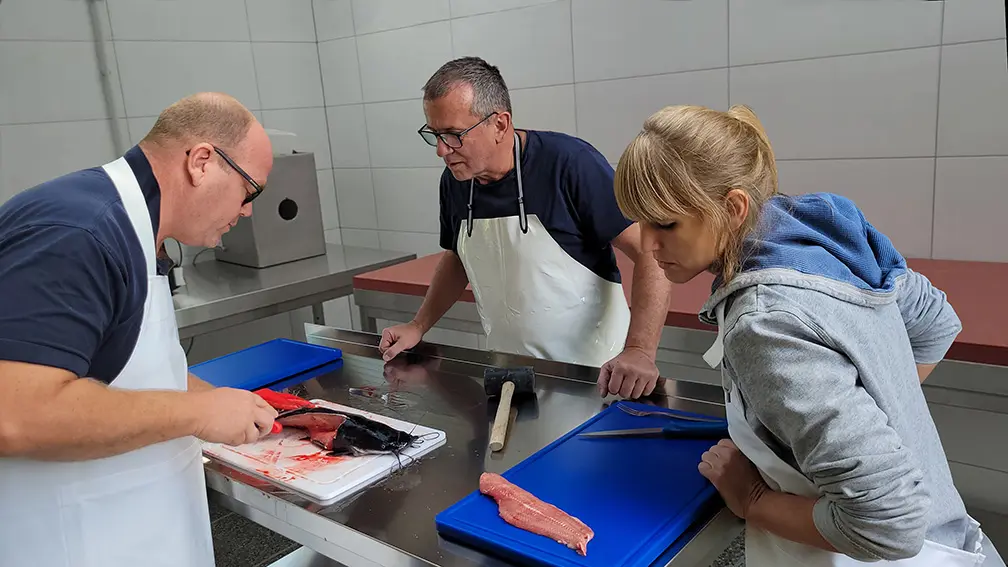

Expand your knowledge
Fish production worldwide
Frequently asked questions
We are asked many questions time and again and we offer you the opportunity to get your own answers here. If you need further information, simply send us a message on ourContact page.
The Aztecs already used agricultural systems in which plants were grown in waters rich in fish in order to utilise the nutrient-rich water. The modern approach combines aquaculture, i.e. the rearing of fish and marine animals, with the cultivation of crops without the use of soil - hydroponics.
But how is an aquaponics system actually constructed?
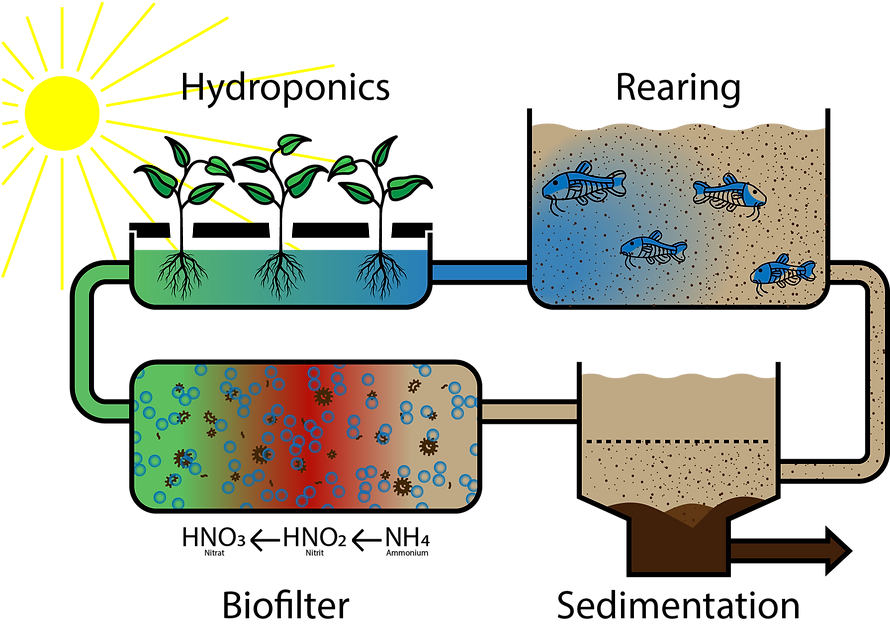
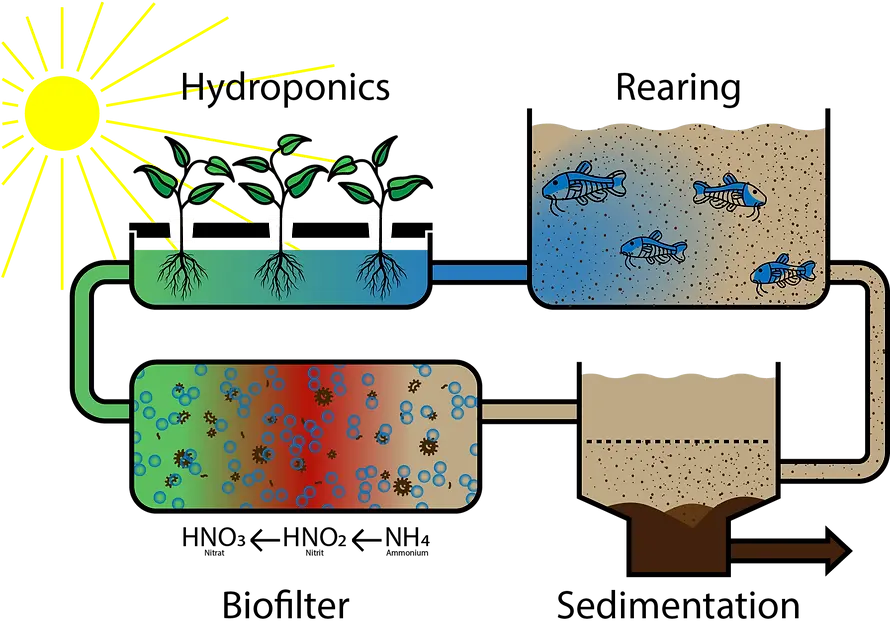
The main components are the fish tanks, the solids filter, the biofilter and the hydroponics system, which are connected to each other via pipes and pumps.
The young fish are placed in the fish tank and fed until they have reached their slaughter weight after 4-6 months. The excrement and faeces that the fish release into the water are pumped into the solids filter.
The suspended particles settle there and can be further utilised as fertiliser. The contaminated water flows further into the biofilter, where bacteria convert the ammonium to nitrite and finally to nitrate using oxygen from the air.
The enriched water now flows into the hydroponics system, where the plants extract the nutrients and purify them. The water then flows back into the fish tank, completing the cycle.
The main advantages of an aquaponics system are
- low fresh water consumption thanks to the closed circuit system
- the low labour input due to the elimination of weed control
- the elimination of pest control measures due to the protected cultivation area
- the saving of additional fertilisers
- the low space requirement
- and the rapid growth of plants and fish due to the positive symbiotic interactions
The cost of building an aquaponics system depends on the technical set-up, the annual production volume of fish and vegetables and the breeds intended for rearing.
An entry-level system with an annual production capacity of 600kg of African catfish and a 15m² greenhouse costs around EUR 10,000 to build yourself.
A commercial system for the annual production volume of 25 tonnes of African catfish and a 100m² greenhouse costs between EUR 100,000 and EUR 300,000 with a large amount of self-construction work. The large difference in costs depends on whether a room is available to house the aquaculture, whether additional processing rooms are required and whether it is possible to connect to an existing heating system.
The values shown are from realised plants in Central Europe in 2023.
This depends heavily on the fattening method and the type of fish.
For African catfish, which are fattened in a recirculation system, fattening costs of around EUR 8 per kg of fillet can be assumed. The largest cost factor here is clearly the fish feed, which accounts for over 50%. The rest is made up of the costs for seedlings, electricity costs, heating costs and costs for processing and packaging.
The time required for an aquaponics system depends largely on the system design and is made up of the following components:
- Fish: Fish feeding (daily): approx. 10 minutes
- System maintenance (weekly): approx. 15 minutes to approx. 1 hour
- Slaughtering (per slaughter day): approx. 2 hours preparation and post-processing plus approx. 3 minutes per fish.
Planting: There is no daily effort as there is no need for watering, fertilising and weeding. The main effort is required for sowing or planting and harvesting. With certain plants, e.g. tomatoes, plant care (thinning out) is also necessary. However, the time required is considerably less than for conventional vegetable cultivation.
This depends on the design of the aquaponics system and the type and quantity of food used for the fish. For systems with a correctly dimensioned and well-functioning biofilter, which converts the substances released by the fish into nitrate, the following quantities can be assumed:
For weak eaters (e.g. lettuce, herbs,...), 1m² of cultivation area per 50g of fish food (for African catfish) is possible. For heavy eaters (e.g. tomatoes, cucumbers,...), 0.5m² of cultivation area per 50g of fish food is possible.
The nitrate levels should be checked regularly and, if they become too high, diluted by adding fresh water.
